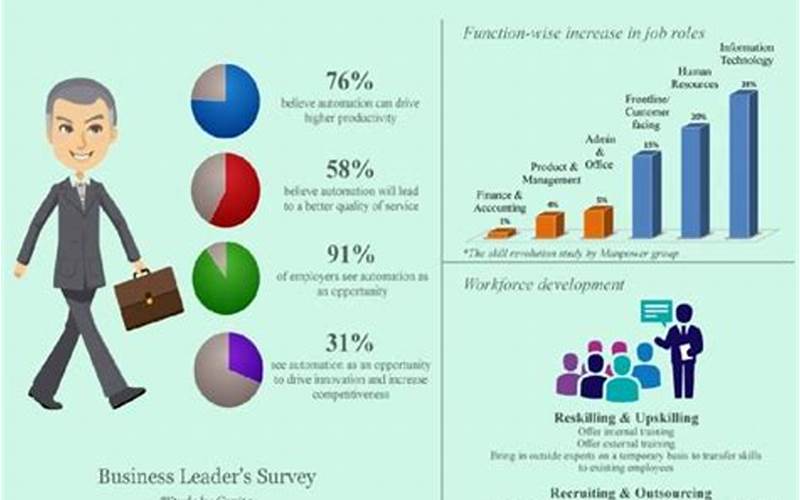
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, workplace automation has become a prominent topic of discussion. As companies strive to streamline their operations and boost efficiency, automation has emerged as a key solution. However, this advancement comes with a significant impact on job roles and the skills required to thrive in the modern workplace.
Contents
- 1 The Rise of Workplace Automation
- 2 Understanding the Impact on Job Roles
- 3 Evolving Skill Sets in the Digital Age
- 4 The Importance of Adaptability
- 5 Reskilling and Upskilling Opportunities
- 6 Redefining Job Satisfaction
- 7 Ethical Considerations in Workplace Automation
- 8 The Future of Job Roles in an Automated World
- 9 Embracing Automation for a Competitive Edge
- 10 Conclusion: Navigating the Automated Workplace
The Rise of Workplace Automation
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, workplace automation has emerged as a game-changer for organizations across various industries. This technological advancement involves the integration of automated systems, software, and robotics into day-to-day operations, aiming to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and reduce human error.
The rise of workplace automation can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, advancements in technology have made automation more accessible and cost-effective for businesses of all sizes. Moreover, the increasing demand for faster and more accurate results has prompted organizations to turn to automation as a solution.
- Starting Your Small Business: A Step-by-Step Guide to Success
- The Evolving Landscape: Navigating Remote and Hybrid Work Models
- Building Success from Scratch: Unraveling the Essence of Business Start-ups
- Nurturing Future Business Leaders: Unleashing Potential through Leadership Development Programs
- Exploring the Nuts and Bolts: Costs and Considerations for Starting a Business
One of the key benefits of workplace automation is the ability to perform repetitive and mundane tasks with minimal human intervention. This allows employees to focus on more complex and value-driven activities that require critical thinking and creativity.
Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity
Automation has the potential to significantly improve efficiency and productivity within an organization. By automating time-consuming tasks, such as data entry, report generation, and inventory management, companies can free up valuable employee time and resources.
Automated systems can work around the clock without the need for breaks or rest, ensuring continuous operation and faster turnaround times. This not only accelerates processes but also enables organizations to meet customer demands more efficiently, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
Reducing Human Error and Increasing Accuracy
Human error is an inherent aspect of any manual task. However, automation minimizes the risk of errors by executing tasks with precision and consistency. Automated systems follow predefined rules and algorithms, reducing the likelihood of mistakes caused by fatigue, distraction, or oversight.
Moreover, automation enables real-time data capture and analysis, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing the possibility of transcription errors. This ensures that organizations have access to accurate and up-to-date information for informed decision-making.
Cost Savings and Resource Optimization
Implementing workplace automation can lead to significant cost savings for organizations. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can reduce labor costs and reallocate resources to more strategic initiatives. This not only improves the bottom line but also allows businesses to invest in areas that drive growth and innovation.
Furthermore, automation helps optimize resource allocation by eliminating inefficiencies and bottlenecks in processes. Automated systems can analyze data, identify patterns, and make recommendations to improve resource utilization, leading to optimized workflows and reduced waste.
In conclusion, workplace automation is revolutionizing the way businesses operate. By enhancing efficiency, reducing errors, and optimizing resource allocation, automation enables organizations to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced digital landscape. However, it is important for businesses to strike a balance between automation and human involvement, ensuring that employees are equipped with the necessary skills to collaborate effectively with automated systems.
Understanding the Impact on Job Roles
As workplace automation continues to advance, it is crucial to understand the impact it has on job roles within organizations. Automation has the potential to reshape traditional job responsibilities and require employees to adapt to new roles and skill requirements.
Job Redefinition and Elimination
Automation often leads to a redefinition of job roles, with some tasks being completely eliminated. Jobs that involve repetitive and routine tasks are most susceptible to automation. For example, data entry, assembly line work, and customer support chatbots are now commonly automated.
While this may create concerns about job security, it also opens up opportunities for employees to take on more complex and strategic roles. Rather than focusing on mundane tasks, workers can engage in higher-value activities that require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity.
Adapting to New Skill Requirements
The introduction of automation necessitates a shift in the skills required to thrive in the modern workplace. Employees need to adapt and acquire new skill sets to complement automated systems effectively.
Technical skills, such as data analysis, programming, and proficiency in using automation tools, become increasingly valuable. Additionally, soft skills such as critical thinking, communication, and adaptability are essential in collaborating with automated systems and working in cross-functional teams.
Upskilling and Reskilling Opportunities
Organizations must invest in upskilling and reskilling programs to ensure their workforce remains relevant in an automated environment. Upskilling involves enhancing existing skills to align with the changing demands of job roles, while reskilling focuses on learning entirely new skills.
Training programs, workshops, and online courses can help employees develop the necessary technical and soft skills required to excel in the automated workplace. By providing these opportunities, organizations empower their workforce to embrace automation and take on new challenges.
Collaboration Between Humans and Machines
Contrary to popular belief, automation is not about replacing humans; it’s about collaboration. Human-machine collaboration allows for a more efficient and productive work environment.
Automated systems handle repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up human employees to focus on tasks that require creativity, emotional intelligence, and strategic decision-making. This partnership allows organizations to leverage the strengths of both humans and machines, leading to improved outcomes and innovation.
In summary, workplace automation brings about significant changes in job roles and the skills required to succeed. While some job roles may be redefined or eliminated, automation offers new avenues for growth and strategic contributions. By adapting to changing skill requirements, upskilling, and fostering collaboration between humans and machines, organizations can navigate the evolving landscape and unlock the full potential of automation.
Evolving Skill Sets in the Digital Age
As workplace automation becomes more prevalent, the skill sets required to thrive in the digital age are also evolving. Employees need to acquire and develop new skills that complement and enhance automated systems, enabling them to remain valuable contributors in the modern workplace.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
With automation generating vast amounts of data, the ability to analyze and interpret data becomes increasingly valuable. Employees skilled in data analysis can extract meaningful insights, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions. This skill is crucial in optimizing processes, identifying opportunities for improvement, and driving innovation.
Programming and Automation Proficiency
A basic understanding of programming languages and automation tools is becoming essential in the digital age. Employees who can write scripts, develop workflows, and automate repetitive tasks are highly sought after. This skill enables individuals to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and leverage automation to their advantage.
Adaptability and Continuous Learning
In an environment where technology and automation rapidly evolve, adaptability and a willingness to learn are key attributes for success. Employees must be open to change, embrace new technologies, and continuously update their skills to remain relevant. Those who can quickly adapt to new systems and processes will thrive in the automated workplace.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
While automation handles routine tasks, critical thinking and problem-solving skills are indispensable. Employees who can analyze complex situations, identify challenges, and propose creative solutions bring immense value to organizations. These skills are particularly important in tasks that involve strategic decision-making and addressing unforeseen issues.
Collaboration and Communication
As automation transforms job roles, effective collaboration and communication skills become crucial for success. Employees must be able to work seamlessly with automated systems, as well as with their human colleagues. Strong communication skills facilitate the exchange of ideas, promote teamwork, and ensure that automated processes align with organizational goals.
Emotional Intelligence and Adaptability
Automation may streamline processes, but it cannot replace human qualities such as empathy, emotional intelligence, and adaptability. Employees who possess these traits can navigate complex interpersonal dynamics, build strong relationships, and adapt to changing circumstances. Emotional intelligence is particularly valuable in roles that involve customer interaction and team management.
In conclusion, the digital age demands a new set of skills to thrive in an automated workplace. Data analysis, programming proficiency, adaptability, critical thinking, collaboration, and emotional intelligence are among the skills that employees should develop to remain competitive. By continuously learning and evolving, individuals can harness the power of workplace automation and contribute effectively to their organizations’ success.
The Importance of Adaptability
In the age of workplace automation, adaptability has become a critical skill for employees to thrive in their roles. The ability to embrace change, learn new technologies, and adapt to evolving job requirements is essential in the ever-changing landscape of automated workplaces.
Embracing Technological Advancements
Automation brings about technological advancements that can significantly transform job roles and processes. Employees who are adaptable are open to learning and embracing these advancements. They are willing to explore new tools, software, and systems to enhance their productivity and contribute effectively in the automated workplace.
Flexibility in Job Responsibilities
Adaptability enables employees to be flexible in their job responsibilities. As automation redefines roles, employees may be required to take on new tasks or collaborate with automated systems. Adaptable individuals are willing to take on these challenges, adjusting their skills and approaches to meet the evolving demands of their roles.
Continuous Learning and Skill Development
Adaptability goes hand in hand with continuous learning and skill development. Adaptable employees actively seek opportunities to expand their knowledge and acquire new skills that align with the changing requirements of their roles. They are committed to staying updated with the latest trends and technologies, ensuring their relevance in the automated workplace.
Embracing Change Management
Change is a constant in the automated workplace, and adaptable employees excel in change management. They understand that automation may lead to process reengineering and organizational restructuring. Adaptable individuals are receptive to changes, proactively identify potential challenges, and collaborate with colleagues and stakeholders to implement smooth transitions.
Problem-Solving in Dynamic Environments
Adaptable employees thrive in dynamic environments where problems and challenges are constantly evolving. They possess strong problem-solving skills and are quick to adapt their approaches as new information or circumstances arise. Adaptable individuals can think on their feet, analyze situations from different perspectives, and propose creative solutions to address emerging issues.
Embracing a Growth Mindset
Adaptability is closely linked to having a growth mindset. Employees with a growth mindset believe that their abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work. They view challenges and setbacks as opportunities for learning and improvement, enabling them to adapt to new situations and grow professionally in the automated workplace.
In conclusion, adaptability is a fundamental skill in the age of workplace automation. Employees who embrace change, continuously learn and develop their skills, and possess problem-solving abilities thrive in the ever-evolving landscape of automated workplaces. By fostering adaptability, organizations can ensure their workforce is equipped to navigate the challenges and harness the opportunities presented by workplace automation.
Reskilling and Upskilling Opportunities
As workplace automation reshapes job roles, organizations must invest in reskilling and upskilling programs to ensure their workforce remains competitive and adaptable. These opportunities allow employees to acquire new skills or enhance existing ones, enabling them to thrive in the automated workplace.
Identifying Skill Gaps
Before implementing reskilling and upskilling initiatives, organizations must identify skill gaps within their workforce. This involves assessing the current skill sets of employees and identifying areas where additional training or development is required. By understanding the skill gaps, organizations can design targeted programs to address specific needs.
Designing Tailored Training Programs
Once skill gaps are identified, organizations can design tailored training programs to address those gaps effectively. These programs may include workshops, seminars, online courses, or on-the-job training. By customizing the training to the specific needs of employees, organizations can maximize the impact of reskilling and upskilling initiatives.
Providing Resources for Continuous Learning
Reskilling and upskilling are not one-time events; they are ongoing processes. Organizations should provide resources for continuous learning to enable employees to stay updated with the latest industry trends and technologies. This may include access to online learning platforms, subscriptions to industry publications, or encouraging participation in professional development conferences or webinars.
Encouraging Cross-Training and Cross-Functional Collaboration
Reskilling and upskilling programs can be enhanced by encouraging cross-training and cross-functional collaboration. By exposing employees to different areas of the organization and allowing them to work on projects outside their immediate domain, organizations foster a culture of continuous learning and skill development. This cross-pollination of skills and knowledge can lead to innovative solutions and a more versatile workforce.
Recognizing and Rewarding Skill Development
Organizations should recognize and reward employees who actively participate in reskilling and upskilling programs. This not only motivates employees to engage in continuous learning but also reinforces the importance of skill development in the automated workplace. Recognition can take the form of promotions, bonuses, or acknowledgment through internal communication channels.
Monitoring and Evaluating the Impact
It is crucial for organizations to monitor and evaluate the impact of reskilling and upskilling programs. This can be done through regular assessments, feedback sessions, or performance evaluations. By tracking the progress of employees and measuring the effectiveness of the programs, organizations can fine-tune their initiatives and ensure they are achieving the desired outcomes.
In conclusion, reskilling and upskilling initiatives play a vital role in preparing employees for the challenges and opportunities presented by workplace automation. By identifying skill gaps, designing tailored training programs, providing continuous learning resources, encouraging cross-training, recognizing skill development, and monitoring the impact, organizations can equip their workforce with the necessary skills to thrive in the automated workplace.
Redefining Job Satisfaction
Workplace automation has the potential to redefine job satisfaction by transforming the nature of work and the tasks employees are responsible for. While automation can eliminate mundane and repetitive tasks, it also introduces new considerations and challenges that impact an employee’s overall job satisfaction.
Eliminating Repetitive and Mundane Tasks
Automation can alleviate employees from repetitive and mundane tasks, allowing them to focus on more engaging and fulfilling work. By delegating routine tasks to automated systems, employees have the opportunity to take on more challenging and intellectually stimulating responsibilities. This shift can lead to increased job satisfaction as employees can devote their time and energy to tasks that require creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
Creating Concerns about Job Security
While automation brings numerous benefits, it can also create concerns about job security. Employees may worry that their roles are at risk of being replaced by automated systems or robots. It is essential for organizations to address these concerns transparently and communicate the long-term vision of automation as a means to enhance productivity and create new opportunities for growth rather than as a threat to job security.
Encouraging Skill Development and Growth
With automation reshaping job roles, employees have the opportunity to develop new skills and grow professionally. Organizations can foster an environment that encourages skill development and provides clear pathways for career progression. Investing in employee training and development programs not only enhances job satisfaction but also equips employees with the skills needed to adapt to the changing demands of the automated workplace.
Strengthening Employee Autonomy and Decision-Making
Automation can empower employees by granting them more autonomy and decision-making power. With routine tasks automated, employees can take ownership of more strategic responsibilities and have a greater impact on organizational outcomes. This increased autonomy and decision-making authority can contribute to job satisfaction by providing a sense of purpose and control over one’s work.
Fostering Collaboration and Teamwork
Automation often requires collaboration between humans and machines. This collaboration can foster a sense of camaraderie and teamwork, as employees work alongside automated systems to achieve common goals. Organizations that foster a collaborative culture and provide opportunities for employees to learn and collaborate with automated systems can enhance job satisfaction and create a positive work environment.
Promoting Work-Life Balance
Automation can also contribute to improved work-life balance. By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, employees can dedicate more time to their personal lives and pursue activities outside of work. Organizations that prioritize work-life balance and provide flexible work arrangements can enhance job satisfaction and employee well-being in the context of workplace automation.
In conclusion, workplace automation can redefine job satisfaction by eliminating repetitive tasks, creating concerns about job security, encouraging skill development and growth, strengthening employee autonomy, fostering collaboration, and promoting work-life balance. By addressing these factors, organizations can ensure that employees find fulfillment and a sense of purpose in their roles within an automated workplace.
Ethical Considerations in Workplace Automation
As workplace automation becomes more prevalent, ethical considerations arise that organizations must address. While automation offers numerous benefits, it also raises concerns related to job displacement, privacy, and the ethical use of data. It is crucial for organizations to navigate these ethical considerations to ensure the responsible implementation of automation.
Job Displacement and Job Security
One of the primary ethical concerns associated with workplace automation is job displacement. As automated systems take over certain tasks, employees may face the risk of losing their jobs or being reassigned to different roles. Organizations must approach automation with a commitment to supporting affected employees through reskilling, retraining, or providing alternative employment opportunities to mitigate the negative impact on job security.
Privacy and Data Protection
Automation often involves the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data. Organizations must prioritize privacy and data protection to ensure that personal and sensitive information is handled responsibly. This involves implementing robust security measures, obtaining informed consent, and adhering to data protection regulations to maintain the trust of employees and customers.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
Automated systems rely on algorithms to make decisions and recommendations. It is essential to address algorithmic bias, which may occur when algorithms produce unfair or discriminatory outcomes due to biased data or flawed algorithms. Organizations must strive for fairness and transparency in the design and deployment of automated systems to ensure equal opportunities and avoid perpetuating biases.
Transparency and Explainability
Transparency and explainability are crucial ethical considerations in workplace automation. Employees should have a clear understanding of how automated systems work, the criteria used for decision-making, and how their performance is evaluated. Transparent communication about the role of automation within the organization fosters trust and addresses concerns related to accountability and fairness.
Social Impact and Inequality
Automation can have a significant social impact, potentially exacerbating inequality if not implemented responsibly. Organizations must consider the broader societal implications of workplace automation and work towards minimizing negative consequences. This may involve collaborating with policymakers, industry peers, and stakeholders to create inclusive strategies that address social inequalities and ensure equitable access to opportunities.
Ethical Use of Automation and AI
The ethical use of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) is of utmost importance. Organizations should establish guidelines and ethical frameworks that govern the use of automation technologies. This includes ensuring that automated systems are used responsibly, without compromising human rights or ethical principles, and that they are aligned with organizational values and societal norms.
In conclusion, workplace automation brings ethical considerations that organizations must navigate to ensure responsible and ethical practices. By addressing job displacement, privacy, algorithmic bias, transparency, social impact, and the ethical use of automation, organizations can harness the benefits of automation while upholding ethical standards and promoting a positive impact on employees and society as a whole.
The Future of Job Roles in an Automated World
The rise of workplace automation has sparked discussions about the future of job roles and the potential impact on employment. While automation may lead to the elimination of certain job roles, it also opens up new opportunities and demands a shift towards roles that require human judgment, critical thinking, and creativity.
Emergence of New Job Roles
As automation takes over routine and repetitive tasks, new job roles emerge to support and collaborate with automated systems. These roles often involve managing, maintaining, and optimizing automated processes. For example, organizations may require automation specialists, data analysts, or AI trainers to ensure the smooth integration and utilization of automated technologies.
Focus on Creativity and Innovation
With automation handling routine tasks, human employees can allocate their time and energy to more creative and innovative endeavors. Job roles that emphasize creativity, problem-solving, and innovation become increasingly valuable. These roles involve thinking critically, identifying new opportunities, and leveraging automation technologies to drive growth and competitiveness.
Importance of Human Interaction and Emotional Intelligence
Automation cannot replicate human qualities such as empathy, emotional intelligence, and interpersonal skills. Job roles that involve direct customer interactions, team collaboration, and leadership will continue to rely on human interaction. These roles require strong communication skills, relationship-building abilities, and the capacity to understand and respond to complex human emotions and needs.
Integration of Automation into Existing Roles
Automation is not always about replacing entire job roles but rather augmenting them. Many existing job roles can benefit from the integration of automation technologies to enhance productivity and efficiency. Employees will need to adapt and develop skills to work seamlessly with automated systems, leveraging their unique human capabilities alongside automation to achieve optimal outcomes.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
In an automated world, continuous learning and adaptation become crucial for long-term employability. Job roles will continue to evolve, and employees must be proactive in acquiring new skills and staying updated with industry trends. Lifelong learning and adaptability are key to remaining relevant and agile in an ever-changing professional landscape.
Collaboration Between Humans and Machines
The future of job roles lies in collaboration between humans and machines. Rather than replacing humans, automation complements human abilities and enhances productivity. Job roles will increasingly involve working alongside automated systems, leveraging their capabilities while bringing human judgment, creativity, and problem-solving skills to the table.
In summary, the future of job roles in an automated world is dynamic and transformative. While some job roles may be eliminated, new opportunities will emerge, emphasizing creativity, innovation, and human interaction. Adaptability, continuous learning, and collaboration between humans and machines will be critical for individuals to thrive in the automated workplace.
Embracing Automation for a Competitive Edge
Rather than fearing automation, organizations should embrace it as a means of gaining a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business landscape. By leveraging automation technologies effectively, businesses can achieve increased efficiency, productivity, and innovation.
Streamlining Operations and Processes
Automation allows organizations to streamline their operations and processes, eliminating manual and time-consuming tasks. By automating routine activities, employees can focus on more strategic and value-added work. This improved efficiency leads to faster turnaround times, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Enhancing Productivity and Accuracy
Automation significantly enhances productivity by enabling employees to accomplish more in less time. Automated systems can perform tasks faster and with greater accuracy, reducing the risk of errors and rework. This increased productivity allows organizations to meet customer demands more efficiently and stay ahead of the competition.
Enabling Data-Driven Decision Making
Automation provides organizations with access to vast amounts of data that can be analyzed and utilized for data-driven decision making. Automated systems can collect, process, and analyze data in real-time, enabling organizations to make informed and strategic decisions. This data-driven approach enhances organizational agility and helps businesses stay ahead of market trends.
Promoting Innovation and Creativity
By automating repetitive tasks, employees can dedicate more time and energy to innovation and creative problem-solving. Automation frees up employees to think outside the box, explore new ideas, and develop innovative solutions. This promotes a culture of innovation within the organization, driving growth and differentiation in the marketplace.
Improving Customer Experience
Automation plays a crucial role in improving the customer experience. Automated systems can provide personalized and efficient services, such as chatbots for customer support or recommendation algorithms for personalized product suggestions. This enhanced customer experience fosters loyalty, attracts new customers, and ultimately contributes to the organization’s competitive advantage.
Adapting to Changing Market Demands
Automation enables organizations to adapt quickly to changing market demands. By automating processes, businesses can scale up or down as needed, respond to market trends, and seize new opportunities. This agility allows organizations to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Unlocking Employee Potential
Automation empowers employees by eliminating mundane and repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on more meaningful and complex work. This not only increases job satisfaction but also unleashes the potential of employees to contribute to the organization’s success. Automation enables employees to leverage their unique skills and capabilities, driving innovation and growth.
In conclusion, embracing automation provides organizations with a competitive edge by streamlining operations, enhancing productivity, enabling data-driven decision making, promoting innovation, improving the customer experience, adapting to changing market demands, and unlocking employee potential. By harnessing the power of automation, businesses can position themselves for long-term success in the digital age.
The rise of workplace automation has brought both opportunities and challenges for organizations and employees alike. As technology continues to advance, it is crucial to navigate the automated workplace effectively and responsibly.
Adapting to Change
Adaptability is key in the automated workplace. Employees must be open to learning new skills, embracing change, and adapting to evolving job requirements. Organizations should foster a culture that encourages continuous learning and provides opportunities for employees to upskill and reskill.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations must be at the forefront of workplace automation. Organizations should prioritize job security, privacy, fairness, transparency, and the responsible use of automation technologies. By addressing these ethical considerations, businesses can ensure a positive and sustainable impact on employees, customers, and society as a whole.
Collaboration between Humans and Machines
The future of work lies in collaboration between humans and machines. Automation is not about replacing humans but rather enhancing their capabilities and productivity. By leveraging automation technologies while utilizing human strengths such as creativity, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence, organizations can achieve optimal outcomes.
Continuous Learning and Skill Development
Continuous learning and skill development are essential in the automated workplace. Employees should embrace lifelong learning, stay updated with industry trends, and acquire new skills that align with the evolving demands of their roles. By investing in employee development, organizations can ensure a skilled and adaptable workforce.
Embracing Automation for Success
Rather than fearing automation, organizations should embrace it as a catalyst for success. Automation brings numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, productivity, and innovation. By leveraging automation technologies effectively, businesses can gain a competitive edge and drive growth in the digital age.
In conclusion, the automated workplace presents opportunities and challenges that organizations and employees must navigate. By fostering adaptability, addressing ethical considerations, promoting collaboration, investing in continuous learning, and embracing automation, businesses can thrive in the ever-changing landscape of work and drive success in the automated world.
In conclusion, workplace automation is revolutionizing the way businesses operate. It has the potential to streamline operations, increase efficiency, and drive innovation. However, it also brings about significant changes in job roles and skill requirements. As organizations embrace automation, they must prioritize adaptability, invest in reskilling and upskilling programs, and address ethical considerations. By doing so, businesses can navigate the automated workplace effectively and unlock the full potential of automation. With the right approach, automation can provide a competitive edge and create a more efficient and productive work environment. As technology continues to advance, it is essential for organizations and employees to embrace change, continuously learn, and collaborate with automated systems. By harnessing the benefits of automation while balancing human capabilities, businesses can thrive in the digital age and shape a successful future.

