Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating world of organizational agility and its crucial role in adapting quickly to market changes. In today’s fast-paced business landscape, organizations must possess the ability to swiftly respond and adjust their strategies to meet shifting market demands. This article will explore the concept of organizational agility, its benefits, and practical tips to cultivate it within your own company. So, let’s dive in and discover how mastering agility can be the key to staying ahead in an ever-evolving market.
Contents
- 1 1. Understanding Organizational Agility
- 2 2. The Benefits of Embracing Agility
- 3 3. Key Elements of an Agile Organization
- 4 4. Agile Leadership: A Catalyst for Change
- 5 5. Agile Talent Management and Skill Development
- 6 6. Nurturing Agile Teams for Success
- 7 7. Agile Project Management: Adapting to Change
- 8 8. Overcoming Barriers to Organizational Agility
- 9 9. Real-World Examples of Agile Organizations
- 10 10. Building a Roadmap for Organizational Agility
1. Understanding Organizational Agility
Before we delve into the intricacies of organizational agility, let’s first establish a clear understanding of what it entails. Organizational agility refers to an organization’s ability to swiftly adapt and respond to changes in the market, technology, or customer needs. It involves embracing flexibility, innovation, and a proactive mindset to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Organizational agility goes beyond simply reacting to market changes; it involves actively seeking opportunities to innovate and lead in the industry. It requires a company-wide commitment to continuous improvement and a willingness to challenge traditional practices and processes.
- Essential Steps for Launching a Successful Cleaning Business
- Unveiling the Essential Startup Costs: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Ultimate Guide to Effortless Business Ventures: Simplifying Startup Success
- Unveiling the Real Costs: Starting a Business on a Shoestring Budget
- The Ultimate Guide to Value-Based and Dynamic Pricing Strategies in Competitive Markets
An agile organization is characterized by its ability to quickly pivot its strategies, products, and services in response to changing customer demands or market dynamics. By being adaptable, organizations can seize emerging opportunities and outmaneuver their competitors.
To achieve organizational agility, companies must foster a culture of collaboration, experimentation, and learning. This involves breaking down silos and encouraging cross-functional teams to work together towards common goals. Agile organizations value transparency, open communication, and feedback, allowing them to quickly identify and address issues or roadblocks.
Furthermore, embracing agile methodologies such as Scrum or Kanban can provide frameworks for organizing work and managing projects in a nimble and iterative manner. These methodologies emphasize incremental delivery, frequent feedback loops, and continuous improvement, enabling organizations to respond rapidly to changing market conditions.
The Benefits of Organizational Agility
The benefits of organizational agility are numerous and far-reaching. By embracing agility, organizations can:
- Enhance customer satisfaction by delivering products and services that align with evolving customer needs and expectations
- Improve time-to-market, allowing them to seize emerging opportunities and gain a competitive edge
- Drive innovation by fostering a culture that encourages experimentation and learning from failures
- Optimize resource allocation by quickly reallocating resources based on changing priorities or market demands
- Boost employee engagement and satisfaction by empowering them to make decisions and contribute to the organization’s success
- Build resilience to navigate through uncertainties and disruptions in the market
Overall, organizational agility is a key driver of success in today’s dynamic business environment. By understanding its importance and the benefits it brings, organizations can proactively embrace agility and position themselves for long-term growth and sustainability.
2. The Benefits of Embracing Agility
Organizations that prioritize agility enjoy a myriad of benefits. These include:
1. Improved Responsiveness to Customer Demands
Agile organizations have the ability to quickly adapt their products, services, and processes to meet changing customer needs. By staying attuned to customer feedback and market trends, they can tailor their offerings to deliver exceptional value and exceed customer expectations.
2. Increased Competitiveness
Agility allows organizations to respond swiftly to competitive threats and seize emerging opportunities. By being proactive and adaptive, they can outmaneuver competitors, gain market share, and solidify their position as industry leaders.
3. Enhanced Innovation
Agile organizations foster a culture of innovation and experimentation. They provide the necessary support and resources for employees to explore new ideas, take calculated risks, and learn from failures. This culture of innovation fuels continuous improvement and drives the development of cutting-edge products and services.
4. Faster Time-to-Market
By embracing agility, organizations can accelerate their time-to-market for new products or features. The ability to quickly respond to customer demands and market trends enables them to deliver solutions ahead of competitors, gaining a significant competitive advantage.
5. Superior Adaptability to Market Shifts
Market conditions can change rapidly, and organizations must be able to adapt just as quickly. Agile organizations are well-positioned to navigate through market shifts, economic uncertainties, and disruptive technologies, ensuring their long-term sustainability.
6. Improved Employee Engagement and Satisfaction
Employees in agile organizations are empowered to make decisions, collaborate cross-functionally, and contribute to the organization’s success. This sense of ownership and autonomy enhances employee engagement, job satisfaction, and retention rates, creating a positive work environment.
7. Optimal Resource Allocation
Organizational agility allows for efficient resource allocation. As market demands change, agile organizations can quickly reallocate resources to align with new priorities or capitalize on emerging opportunities. This flexibility maximizes resource utilization and minimizes waste.
In summary, embracing agility offers organizations a host of benefits, including improved customer responsiveness, increased competitiveness, enhanced innovation, faster time-to-market, superior adaptability, improved employee engagement, and optimal resource allocation. By understanding these benefits, organizations can make a compelling case for embracing agility as a strategic imperative.
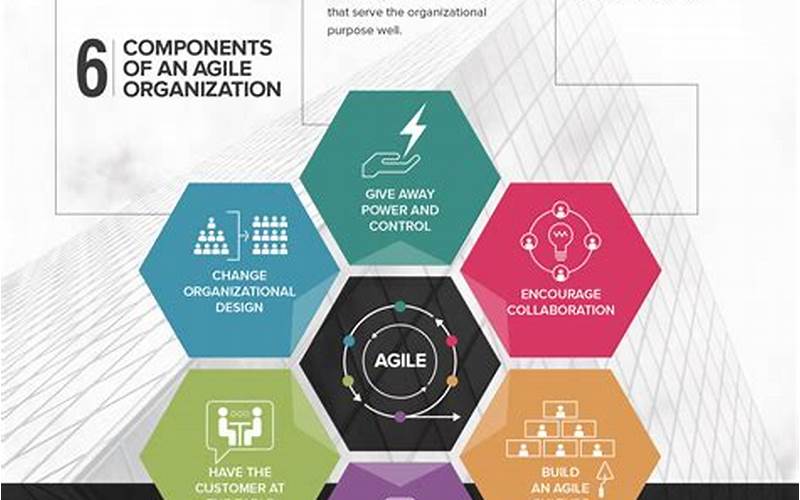
3. Key Elements of an Agile Organization
Building an agile organization requires the integration of several key elements. These elements provide the foundation for agility to flourish within an organization:
1. Culture of Collaboration and Continuous Learning
An agile organization fosters a culture of collaboration, where teams work together across departments and hierarchies. They promote open communication, knowledge sharing, and a continuous learning mindset. This collaborative culture encourages innovation, adaptability, and the exchange of diverse perspectives.
2. Empowerment and Decision-Making
Agile organizations empower employees at all levels to make decisions and take ownership of their work. This decentralization of decision-making promotes faster response times, fosters a sense of ownership, and encourages accountability. It allows teams to adapt quickly to changing circumstances without unnecessary bureaucracy.
3. Agile Methodologies and Practices
Agile organizations embrace methodologies such as Scrum or Kanban to organize and manage their work. These methodologies promote iterative and incremental approaches to project management, allowing teams to deliver value in shorter cycles. Agile practices, such as daily stand-up meetings and retrospectives, facilitate transparency, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
4. Technology Enablement
Technology plays a crucial role in enabling agility within organizations. Agile organizations leverage technology to facilitate rapid decision-making, streamline communication, and improve collaboration. They invest in tools and platforms that support agile practices, such as project management software, collaboration tools, and data analytics systems.
5. Cross-Functional Teams
Agile organizations encourage the formation of cross-functional teams, where individuals with diverse skills and expertise come together to work towards a common goal. These teams have a broader understanding of the organization’s objectives and can adapt more easily to changing requirements. Cross-functional collaboration also leads to better problem-solving and innovation.
6. Agile Leadership
Leadership plays a critical role in fostering agility within an organization. Agile leaders lead by example, embodying the values of agility and embracing a growth mindset. They provide guidance, empower their teams, and remove obstacles that hinder agility. Agile leaders also create a safe environment where innovation, experimentation, and learning are encouraged.
By incorporating these key elements into their organizational structure and practices, businesses can create an environment that nurtures agility. These elements work together to enable organizations to respond quickly to market changes, capitalize on new opportunities, and cultivate a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
4. Agile Leadership: A Catalyst for Change
Leadership plays a pivotal role in driving organizational agility. Agile leaders possess the following qualities that contribute to the success of an agile organization:
1. Transparency and Open Communication
Agile leaders value transparency and foster open communication within the organization. They share information about the company’s vision, goals, and strategies, ensuring that everyone understands the direction and can align their efforts accordingly. This transparency builds trust and empowers employees to make informed decisions.
2. Empowerment and Trust
Agile leaders empower their teams by trusting them to make decisions and take ownership of their work. They provide guidance and support, but also give autonomy and freedom to experiment. By trusting their teams, agile leaders enable innovation and create an environment where individuals can thrive and contribute their best ideas.
3. Encouragement of Experimentation
Agile leaders encourage experimentation and embrace a “fail fast, learn fast” mentality. They recognize that not every idea will be successful, but they see failures as valuable learning opportunities. Agile leaders create a safe environment where employees can take risks, learn from their mistakes, and continuously improve their approaches.
4. Collaboration and Team Empowerment
Agile leaders foster a collaborative culture and empower their teams to work together towards common goals. They break down silos and encourage cross-functional collaboration, ensuring that different perspectives and expertise are leveraged to find the best solutions. Agile leaders facilitate effective communication, remove barriers, and provide the necessary resources for teams to succeed.
5. Continuous Learning and Growth Mindset
Agile leaders embody a continuous learning mindset and encourage their teams to do the same. They invest in professional development opportunities, provide training, and support employees in acquiring new skills. Agile leaders seek feedback, learn from failures, and continuously improve their own leadership abilities.
6. Adaptability and Flexibility
Agile leaders are adaptable and flexible in their approach. They embrace change and are willing to pivot strategies based on new information or market shifts. Agile leaders inspire their teams to be resilient and adaptable, guiding them through times of uncertainty and encouraging a mindset that embraces change as an opportunity for growth.
Agile leadership is essential for fostering a culture of agility within an organization. By embodying these qualities, leaders can inspire and empower their teams to embrace agility, adapt quickly to market changes, and drive the organization toward sustained success.
5. Agile Talent Management and Skill Development
In an agile organization, talent management takes on a new dimension. Here are some key aspects of agile talent management and skill development:
1. Skill Development and Continuous Learning
Agile organizations prioritize skill development and continuous learning. They provide employees with opportunities to acquire new skills and stay updated with the latest industry trends. This can include training programs, workshops, conferences, and mentorship initiatives.
2. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Agile organizations encourage cross-functional collaboration, allowing employees to work with individuals from different departments or areas of expertise. This collaboration enhances skill development by exposing employees to diverse perspectives, fostering creativity, and expanding their knowledge base.
3. Growth Mindset and Innovation
Agile organizations cultivate a growth mindset, where employees are encouraged to embrace challenges, take risks, and learn from failures. This mindset fuels innovation and encourages employees to continuously improve their skills and explore new approaches to problem-solving.
4. Agile Performance Management
Traditional performance management processes may not align well with the agility of an organization. Agile organizations adopt performance management practices that focus on frequent feedback, continuous improvement, and goal alignment. This ensures that employees are recognized for their contributions and provided with the necessary support to develop their skills.
5. Team Empowerment and Autonomy
Agile organizations empower their teams to make decisions and take ownership of their work. This empowerment fosters skill development as employees have the freedom to explore their strengths, experiment with new ideas, and develop their expertise in their respective roles.
6. Agile Recruitment and Onboarding
Agile organizations prioritize recruitment and onboarding processes that identify and attract individuals with agile mindsets and the potential to adapt to change. They focus on hiring individuals with a diverse set of skills and experiences, ensuring that teams have the necessary capabilities to respond to market changes effectively.
By focusing on talent management and skill development, agile organizations create an environment that nurtures the growth and development of their employees. This, in turn, enhances the organization’s overall agility, adaptability, and ability to respond to market changes.
6. Nurturing Agile Teams for Success
Agile teams are the building blocks of an agile organization. Here are some key strategies for nurturing and empowering agile teams:
1. Self-Organization and Autonomy
Agile teams thrive when they have the autonomy to make decisions and self-organize. Providing teams with the freedom to plan their work, collaborate, and make decisions empowers them to take ownership and accountability for their outcomes.
2. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Agile teams are composed of individuals with diverse skills and expertise. Encouraging cross-functional collaboration allows team members to leverage their respective strengths, learn from one another, and collectively solve complex problems. This collaboration fosters innovation and a shared sense of responsibility for team success.
3. Iterative and Incremental Delivery
Agile teams deliver value in short iterations, allowing for frequent feedback and continuous improvement. Breaking down work into smaller, manageable chunks enables teams to adapt to changing requirements and customer feedback more effectively. This iterative approach also helps teams identify and address issues early in the development process.
4. Clear Goals and Priorities
Agile teams need clear goals and priorities to align their efforts. The organization should communicate the vision, objectives, and priorities to the team, ensuring everyone understands the desired outcomes. This clarity enables teams to focus their efforts, make informed decisions, and deliver value in line with organizational goals.
5. Continuous Learning and Knowledge Sharing
Agile teams thrive in an environment that encourages continuous learning and knowledge sharing. Providing opportunities for team members to acquire new skills, attend training sessions, and share their learnings fosters personal and collective growth. This culture of learning enhances the team’s ability to adapt to new challenges and seize opportunities.
6. Supportive Leadership and Coaching
Leadership plays a crucial role in supporting and coaching agile teams. Agile leaders provide guidance, remove obstacles, and act as mentors to enable team success. They create a safe environment where teams can experiment, learn from failures, and continuously improve their processes and performance.
By nurturing and empowering agile teams, organizations can harness the collective intelligence and creativity of their employees. These teams become highly adaptable, collaborative, and capable of delivering exceptional results in a rapidly changing business landscape.
7. Agile Project Management: Adapting to Change
Traditional project management approaches often struggle to keep up with the fast-paced nature of market changes. Agile project management methodologies provide a more flexible and adaptive approach. Here are key aspects of agile project management:
1. Iterative Planning and Delivery
Agile project management focuses on iterative planning and delivery. Instead of detailed upfront planning, projects are broken down into smaller increments or iterations. Each iteration delivers a working product or feature, allowing for continuous feedback and adaptation.
2. Customer Collaboration
Agile project management emphasizes customer collaboration throughout the project lifecycle. Customers or stakeholders are involved in providing feedback, setting priorities, and validating the delivered increments. This collaboration ensures that the project aligns with customer needs and expectations.
3. Self-Organizing and Cross-Functional Teams
Agile project management relies on self-organizing and cross-functional teams. These teams have the autonomy to plan and execute the work, making decisions collectively. The combination of diverse skills within the team enables them to deliver value and adapt to changing requirements.
4. Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
Agile project management promotes a culture of continuous improvement. Through retrospectives and regular reflection, teams identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance their processes and performance. This iterative approach allows teams to adapt to changing circumstances effectively.
5. Embracing Change
Agile project management embraces change as a natural part of the project. Instead of resisting change, agile teams are prepared to accommodate new requirements or insights. This flexibility allows projects to respond quickly to market changes or customer feedback, ensuring that the delivered product meets the evolving needs.
6. Effective Communication and Collaboration
Communication and collaboration are essential in agile project management. Daily stand-up meetings, regular communication channels, and visual management tools facilitate effective communication within the team. Collaboration is encouraged to foster a shared understanding and promote collective decision-making.
By adopting agile project management methodologies, organizations can improve their ability to adapt to changing requirements, deliver value incrementally, and ensure customer satisfaction. Agile project management provides a framework that enables teams to navigate through uncertainties and deliver high-quality results in an efficient and adaptive manner.
8. Overcoming Barriers to Organizational Agility
While the benefits of organizational agility are clear, implementing it can be challenging. Here are some common barriers that organizations may face and strategies to overcome them:
1. Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common barrier to organizational agility. To overcome this, organizations should foster a culture of openness and transparency. Communicating the benefits of agility, involving employees in decision-making, and providing support and training can help alleviate resistance and create buy-in.
2. Siloed Departments and Hierarchical Structures
Siloed departments and hierarchical structures can hinder agility by impeding collaboration and decision-making. Breaking down silos and promoting cross-functional collaboration is essential. Encouraging communication and cooperation among teams, creating cross-functional projects, and flattening organizational hierarchies can help foster agility.
3. Lack of Agility in Decision-Making Processes
Slow decision-making processes can hinder agility. Streamlining decision-making by empowering teams, clarifying decision-making authority, and providing guidelines for decision-making can help organizations respond swiftly to market changes. Implementing agile decision-making frameworks, such as decentralized decision-making or rapid experimentation, can also enhance agility.
4. Inflexible Systems and Processes
Outdated systems and rigid processes can impede agility. To overcome this, organizations should review and adapt their systems and processes to enable flexibility and responsiveness. Implementing agile methodologies, leveraging technology, and regularly evaluating and refining processes can help remove barriers to agility.
5. Lack of Agile Mindset and Skills
Organizational agility requires an agile mindset and the necessary skills. Investing in training and development programs that focus on agility, fostering a growth mindset, and providing opportunities for employees to acquire new skills can help build the capabilities needed for agility. Encouraging a culture of learning and experimentation is also crucial.
6. Insufficient Support from Leadership
Leadership support is vital for driving organizational agility. Leaders should champion agility, communicate its importance, and lead by example. They should provide the necessary resources, support agile initiatives, and empower teams to make decisions. A supportive leadership culture encourages and reinforces the adoption of agility throughout the organization.
By identifying and addressing these barriers, organizations can create an environment that fosters and sustains agility. Overcoming these challenges requires a concerted effort, strong leadership, and a commitment to continuous improvement and adaptation.
9. Real-World Examples of Agile Organizations
Examining real-world examples of organizations that have successfully embraced agility can provide valuable insights and inspiration. Here are a few notable examples:
1. Spotify
Spotify, the popular music streaming platform, is known for its agile approach to product development. They organize their teams into small, autonomous squads that work on specific features or areas. These squads have a high degree of autonomy, make their own decisions, and collaborate closely with other squads. This agile structure allows Spotify to continuously iterate and improve its product offerings.
2. Amazon
Amazon, the e-commerce giant, has built agility into its DNA. The company is known for its customer-centric approach and its ability to rapidly adapt to changing market conditions. Amazon uses agile practices, such as frequent deployments, continuous integration, and a culture of experimentation. This agility enables them to quickly test new ideas, launch new products, and stay ahead in the highly competitive e-commerce industry.
3. Netflix
Netflix, the leading streaming platform, is renowned for its agile culture and customer-focused mindset. They embrace a test-and-learn approach, where they constantly experiment with new features, algorithms, and content recommendations. Netflix uses data analytics to gather insights and make data-driven decisions. This agility has allowed them to continuously innovate and disrupt the entertainment industry.
4. Zappos
Zappos, the online shoe and clothing retailer, is known for its agile and customer-centric culture. They prioritize employee empowerment, encouraging individuals to take ownership and make decisions that benefit customers. Zappos fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, where employees are encouraged to experiment and learn from failures. This agility has contributed to their success in delivering exceptional customer service and building a loyal customer base.
5. Google
Google, the technology giant, embraces agility in its product development and organizational practices. They use agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, to manage projects and foster collaboration. Google encourages a culture of innovation and creativity, allowing employees to dedicate a portion of their time to work on their own projects. This agile approach has enabled Google to continuously release new products and stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
These real-world examples demonstrate the diverse ways in which organizations can embrace agility and thrive in dynamic industries. By studying their approaches, organizations can gain valuable insights and learn from their successes to cultivate their own agile practices.
10. Building a Roadmap for Organizational Agility
Embarking on the journey towards organizational agility requires a well-defined roadmap. Here are key steps to consider when building a roadmap for organizational agility:
1. Assess the Current State of Agility
Start by assessing the current state of agility within your organization. Identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas that require improvement. This assessment will provide a baseline and help determine the specific focus areas for building agility.
2. Define Goals and Metrics
Clearly define the goals and desired outcomes for becoming an agile organization. Set measurable metrics to track progress and evaluate the effectiveness of your agility initiatives. These goals and metrics will guide your efforts and provide a clear direction.
3. Foster a Culture of Agility
Culture plays a critical role in organizational agility. Foster a culture that values innovation, collaboration, and continuous learning. Encourage open communication, experimentation, and taking calculated risks. Recognize and reward behaviors that promote agility.
4. Provide Training and Support
Invest in training and development programs to equip employees with the skills and knowledge needed for agility. Provide support for individuals and teams as they navigate the changes associated with agility. This support can include coaching, mentoring, and resources for continuous learning.
5. Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
Promote cross-functional collaboration and break down silos within the organization. Encourage teams from different departments to work together, share knowledge, and collaborate on projects. This cross-functional collaboration enhances agility by leveraging diverse perspectives and expertise.
6. Implement Agile Methodologies and Practices
Adopt agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, to manage projects and workflows. Implement agile practices, such as daily stand-up meetings, retrospectives, and iterative planning. These methodologies and practices provide a framework for agility and enable teams to adapt quickly to changes.
7. Continuously Evaluate and Adapt
Organizational agility is not a one-time effort but an ongoing journey. Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of your agility initiatives and make adjustments as needed. Encourage a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability to ensure sustained success in a rapidly changing business landscape.
By following these steps and building a roadmap for organizational agility, you can create a strategic plan to foster and sustain agility within your organization. Remember that agility requires commitment, perseverance, and a willingness to embrace change as opportunities for growth and innovation.
In conclusion, organizational agility is crucial for businesses to adapt quickly to market changes, stay competitive, and drive innovation. By embracing agility, organizations can enhance their responsiveness to customer demands, increase their competitiveness, and improve their time-to-market. Agile organizations foster a culture of collaboration, empower their teams, and embrace continuous learning and improvement. They overcome barriers to agility, such as resistance to change and inflexible processes, by fostering a supportive leadership culture and embracing agile methodologies.
Real-world examples of agile organizations, such as Spotify, Amazon, Netflix, Zappos, and Google, demonstrate the effectiveness of agility in achieving success in dynamic industries. These organizations prioritize customer collaboration, foster innovation, and empower their teams to make decisions and adapt to changing circumstances.
Building a roadmap for organizational agility involves assessing the current state of agility, defining goals and metrics, fostering a culture of agility, providing training and support, fostering cross-functional collaboration, implementing agile methodologies and practices, and continuously evaluating and adapting. By following these steps, organizations can navigate the journey towards agility and position themselves for long-term growth and sustainability in an ever-changing business landscape.
So, embrace organizational agility, empower your teams, and foster a culture that embraces change and continuous improvement. By doing so, you can position your organization to thrive and succeed in the face of market changes and emerging opportunities.

